
-
 UK PM's top aide quits in scandal over Mandelson links to Epstein
UK PM's top aide quits in scandal over Mandelson links to Epstein
-
Reed continues Gulf romp with victory in Qatar

-
 Conservative Thai PM heading for election victory: projections
Conservative Thai PM heading for election victory: projections
-
Heartache for Olympic downhill champion Johnson after Vonn's crash

-
 Takaichi on course for landslide win in Japan election
Takaichi on course for landslide win in Japan election
-
Wales coach Tandy will avoid 'knee-jerk' reaction to crushing England loss

-
 Sanae Takaichi, Japan's triumphant first woman PM
Sanae Takaichi, Japan's triumphant first woman PM
-
England avoid seismic shock by beating Nepal in last-ball thriller

-
 Karl defends Olympic men's parallel giant slalom crown
Karl defends Olympic men's parallel giant slalom crown
-
Colour and caution as banned kite-flying festival returns to Pakistan

-
 England cling on to beat Nepal in last-ball thriller
England cling on to beat Nepal in last-ball thriller
-
UK foreign office to review pay-off to Epstein-linked US envoy

-
 England's Arundell eager to learn from Springbok star Kolbe
England's Arundell eager to learn from Springbok star Kolbe
-
Czech snowboard great Ledecka fails in bid for third straight Olympic gold

-
 Expectation, then stunned silence as Vonn crashes out of Olympics
Expectation, then stunned silence as Vonn crashes out of Olympics
-
Storm-battered Portugal votes in presidential election run-off

-
 Breezy Johnson wins Olympic downhill gold, Vonn crashes out
Breezy Johnson wins Olympic downhill gold, Vonn crashes out
-
Vonn's Olympic dream cut short by downhill crash

-
 French police arrest five over crypto-linked magistrate kidnapping
French police arrest five over crypto-linked magistrate kidnapping
-
Late Jacks flurry propels England to 184-7 against Nepal

-
 Vonn crashes out of Winter Olympics, ending medal dream
Vonn crashes out of Winter Olympics, ending medal dream
-
All-new Ioniq 3 coming in 2026

-
 New Twingo e-tech is at the starting line
New Twingo e-tech is at the starting line
-
New Ypsilon and Ypsilon hf

-
 The Cupra Raval will be launched in 2026
The Cupra Raval will be launched in 2026
-
New id.Polo comes electric

-
 Iran defies US threats to insist on right to enrich uranium
Iran defies US threats to insist on right to enrich uranium
-
Seifert powers New Zealand to their record T20 World Cup chase

-
 Naib's fifty lifts Afghanistan to 182-6 against New Zealand
Naib's fifty lifts Afghanistan to 182-6 against New Zealand
-
Paul Thomas Anderson wins top director prize for 'One Battle After Another'

-
 De Beers sale drags in diamond doldrums
De Beers sale drags in diamond doldrums
-
NFL embraces fashion as league seeks new audiences

-
 What's at stake for Indian agriculture in Trump's trade deal?
What's at stake for Indian agriculture in Trump's trade deal?
-
Real Madrid can wait - Siraj's dream night after late T20 call-up

-
 Castle's monster night fuels Spurs, Rockets rally to beat Thunder
Castle's monster night fuels Spurs, Rockets rally to beat Thunder
-
Japan votes in snow-hit snap polls as Takaichi eyes strong mandate

-
 Pakistan's capital picks concrete over trees, angering residents
Pakistan's capital picks concrete over trees, angering residents
-
Berlin's crumbling 'Russian houses' trapped in bureaucratic limbo

-
 Neglected killer: kala-azar disease surges in Kenya
Neglected killer: kala-azar disease surges in Kenya
-
Super Bowl set for Patriots-Seahawks showdown as politics swirl

-
 Sengun shines as Rockets rally to beat NBA champion Thunder
Sengun shines as Rockets rally to beat NBA champion Thunder
-
Matsuyama grabs PGA Phoenix Open lead with Hisatsune one back

-
 Washington Post CEO out after sweeping job cuts
Washington Post CEO out after sweeping job cuts
-
Haiti's transitional council hands power to PM

-
 N. Korea to hold party congress in February, first since 2021
N. Korea to hold party congress in February, first since 2021
-
Thailand votes after three leaders in two years

-
 Swiss joy as Von Allmen wins first gold of Winter Olympics
Swiss joy as Von Allmen wins first gold of Winter Olympics
-
George backs England to 'kick on' after Six Nations rout of Wales

-
 Malinin upstaged as Japan keep pressure on USA in skating team event
Malinin upstaged as Japan keep pressure on USA in skating team event
-
Vail's golden comets Vonn and Shiffrin inspire those who follow


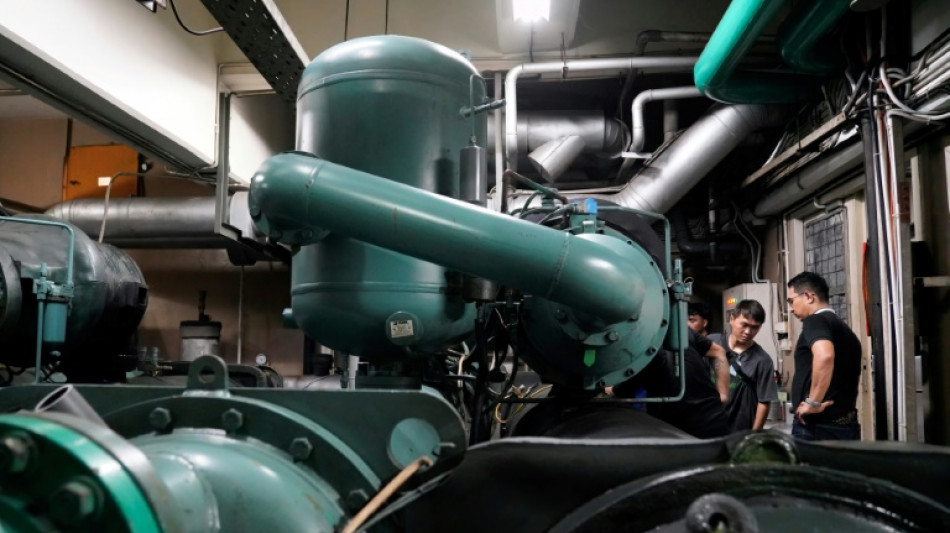
In Indonesia, a start-up captures coolants to stop global warming
In the basement of a Jakarta housing complex, surrounded by the silver piping of the air-conditioning system, Indonesian technician Ari Sobaruddin is doing his part to tackle climate change.
Ari and his colleagues will spend 12 hours capturing AC refrigerant to stop this "super-pollutant" -- thousands of times more potent than carbon dioxide -- from leaking into the atmosphere.
It is plodding, sweaty work, but Ari, a member of climate startup Recoolit, does not mind.
"I love it because it's about preserving nature, saving nature," the 30-year-old technician told AFP.
Recoolit began working in Indonesia in 2021 to tackle what it considers an often-overlooked contributor to climate change: refrigerants.
These gases found in air-conditioners, fridges and cars are an old environmental problem.
In the 1970s, research showed refrigerants called chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) were destroying the ozone layer.
Countries agreed to phase them out under a deal that came into force in 1989.
While their replacements, particularly hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), are less harmful to the ozone layer, they still have major climate-warming properties.
"And those are in AC units, in the form of refrigerant banks... everywhere in developing countries right now," said Recoolit's head of operations Yosaka Eka Putranta.
- 'Growing problem' -
There are international agreements to phase out HFCs too, but, particularly in developing countries, they will be in use for decades yet.
Demand is increasing as climate change fuels record temperatures and expanding middle classes seek cooling and refrigeration.
"It is a growing problem because we need our indoor environments to be more resilient to climate change," said Robyn Schofield, associate professor of atmospheric chemistry at the University of Melbourne.
HFCs are expected to account for between 7 and 19 percent of greenhouse gas emissions by 2050, according to the United Nations.
The risk comes during maintenance or disposal, when refrigerants like the HFC Ari is capturing can be released accidentally or on purpose.
In Indonesia, as in most countries, this venting is illegal, but enforcement is limited.
"It's odourless, we cannot trace it. (Capturing) it takes so much resources. The machine, the people," said Recoolit's senior business development manager Erik Cahyanta.
"So some people just release it."
Recoolit trains, equips and incentivises technicians to capture refrigerant so it can be destroyed.
Technicians get 50,000 rupiah ($3) per kilogram of recovered refrigerant, which Recoolit sends to a government-approved cement kiln or municipal incinerator to be destroyed.
While refrigerant can be recycled or reused, Recoolit argues this is imperfect.
"Who's going to guarantee that when the refrigerants are injected again... they are going to stay there without another venting?" said Yosaka.
- Big tech interest -
Recoolit sells carbon credits based on the amount of refrigerant it destroys, priced at $75 a unit.
Carbon credits have faced criticism in recent years, and Benja Faecks of Carbon Market Watch warned that "offsetting" can give the impression "that emissions can simply be erased through financial transactions".
This allows "polluters to claim 'carbon neutrality' or 'negating ongoing emissions' without actually reducing their own emissions," she told AFP.
Recoolit argues its carbon credits are robust because it measurably destroys a climate-warming gas.
While many carbon credits are sold on exchanges with third-party verification, Recoolit sells directly to buyers and uses a credit methodology developed by the Carbon Containment Lab, a nonprofit spun out from Yale University.
Yosaka said canisters are sampled, and analysis is then done by the region's only qualified lab, in Malaysia, to confirm the contents are refrigerants.
Destruction facilities pass a "trial burn test" confirming they can break down refrigerants.
Recoolit also pays less than the market price for coolants to avoid creating a market for new refrigerants.
Refrigerant destruction remains a relatively small part of the carbon market. Existing players include US-based Tradewater, which grew out of California's state-level emissions caps and has worked in Latin America and Africa.
But Recoolit has attracted attention from one of the market's biggest corporate players: Google.
Earlier this year, the tech giant announced a partnership with Recoolit and a second company to prevent emissions equivalent to one million tons of carbon dioxide.
Google says it wants to help Recoolit scale up operations and expand outside Indonesia.
Some critics say refrigerant capture should simply be enforced by government policy, but Recoolit argues it is filling a real-world gap unlikely to be addressed otherwise.
And Schofield said the need for refrigerant capture is significant.
"As a climate action... it's a very good one," she said.
"I wish we had more of it."
E.Ramalho--PC
