-
 Curling kicks off sports programme at 2026 Winter Olympics
Curling kicks off sports programme at 2026 Winter Olympics
-
Preventative cholera vaccination resumes as global supply swells: WHO

-
 Wales' Macleod ready for 'physical battle' against England in Six Nations
Wales' Macleod ready for 'physical battle' against England in Six Nations
-
Xi calls for 'mutual respect' with Trump, hails ties with Putin

-
 'All-time great': Maye's ambitions go beyond record Super Bowl bid
'All-time great': Maye's ambitions go beyond record Super Bowl bid
-
Shadow over Vonn as Shiffrin, Odermatt headline Olympic skiing

-
 US seeks minerals trade zone in rare Trump move with allies
US seeks minerals trade zone in rare Trump move with allies
-
Ukraine says Abu Dhabi talks with Russia 'substantive and productive'

-
 Brazil mine disaster victims in London to 'demand what is owed'
Brazil mine disaster victims in London to 'demand what is owed'
-
AI-fuelled tech stock selloff rolls on

-
 White says time at Toulon has made him a better Scotland player
White says time at Toulon has made him a better Scotland player
-
Washington Post announces 'painful' job cuts

-
 All lights are go for Jalibert, says France's Dupont
All lights are go for Jalibert, says France's Dupont
-
Artist rubs out Meloni church fresco after controversy

-
 Palestinians in Egypt torn on return to a Gaza with 'no future'
Palestinians in Egypt torn on return to a Gaza with 'no future'
-
US removing 700 immigration officers from Minnesota

-
 Who is behind the killing of late ruler Gaddafi's son, and why now?
Who is behind the killing of late ruler Gaddafi's son, and why now?
-
Coach Thioune tasked with saving battling Bremen

-
 Russia vows to act 'responsibly' once nuclear pact with US ends
Russia vows to act 'responsibly' once nuclear pact with US ends
-
Son of Norway's crown princess admits excesses but denies rape

-
 Vowles dismisses Williams 2026 title hopes as 'not realistic'
Vowles dismisses Williams 2026 title hopes as 'not realistic'
-
'Dinosaur' Glenn chasing skating gold in first Olympics

-
 Gaza health officials say strikes kill 23 after Israel says shots wounded officer
Gaza health officials say strikes kill 23 after Israel says shots wounded officer
-
Italy foils Russian cyberattacks targeting Olympics

-
 Figure skating favourite Malinin feeling 'the pressure' in Milan
Figure skating favourite Malinin feeling 'the pressure' in Milan
-
Netflix film probes conviction of UK baby killer nurse

-
 Timber hopes League Cup can be catalyst for Arsenal success
Timber hopes League Cup can be catalyst for Arsenal success
-
China calls EU 'discriminatory' over probe into energy giant Goldwind

-
 Sales warning slams Ozempic maker Novo Nordisk's stock
Sales warning slams Ozempic maker Novo Nordisk's stock
-
Can Vonn defy ACL rupture to win Olympic medal?

-
 Breakthrough or prelude to attack? What we know about Iran-US talks
Breakthrough or prelude to attack? What we know about Iran-US talks
-
German far-right MP detained over alleged Belarus sanctions breach

-
 MSF says its hospital in South Sudan hit by government air strike
MSF says its hospital in South Sudan hit by government air strike
-
Merz heads to Gulf as Germany looks to diversify trade ties

-
 Selection process for future Olympic hosts set for reform
Selection process for future Olympic hosts set for reform
-
Serbian minister on trial over Trump-linked hotel plan

-
 UK PM says Mandelson 'lied', regrets appointing him US envoy
UK PM says Mandelson 'lied', regrets appointing him US envoy
-
Cochran-Siegle tops first Olympic downhill training

-
 Gaza health officials say strikes kill 21 after Israel says shots wounded officer
Gaza health officials say strikes kill 21 after Israel says shots wounded officer
-
Injured Vonn's Olympic bid is 'inspirational', ski stars say

-
 Albania arrests 20 for toxic waste trafficking
Albania arrests 20 for toxic waste trafficking
-
US-Africa trade deal renewal only 'temporary breather'

-
 Mir sets pace on Sepang day two, Yamaha absent
Mir sets pace on Sepang day two, Yamaha absent
-
Xi, Putin hail 'stabilising' China-Russia alliance

-
 GSK boosted by specialty drugs, end to Zantac fallout
GSK boosted by specialty drugs, end to Zantac fallout
-
UK's ex-prince leaves Windsor home amid Epstein storm: reports

-
 Sky is the limit for Ireland fly-half Prendergast, says captain Doris
Sky is the limit for Ireland fly-half Prendergast, says captain Doris
-
Feyi-Waboso reminds England great Robinson of himself

-
 Starmer faces MPs as pressure grows over Mandelson scandal
Starmer faces MPs as pressure grows over Mandelson scandal
-
HRW urges pushback against 'aggressive superpowers'

| CMSC | -0.51% | 23.54 | $ | |
| CMSD | -0.5% | 23.82 | $ | |
| BCC | 4.74% | 89.16 | $ | |
| JRI | -0.13% | 13.103 | $ | |
| GSK | 6.95% | 57.325 | $ | |
| RIO | -1.07% | 95.35 | $ | |
| BCE | 0.97% | 26.355 | $ | |
| NGG | 2.14% | 88.12 | $ | |
| RBGPF | 0.12% | 82.5 | $ | |
| BTI | -0.28% | 61.7 | $ | |
| AZN | 2.59% | 189.215 | $ | |
| RYCEF | -2.1% | 16.65 | $ | |
| BP | 0.98% | 39.205 | $ | |
| RELX | -2.23% | 29.845 | $ | |
| VOD | 2.59% | 15.655 | $ | |
| SCS | 0.12% | 16.14 | $ |

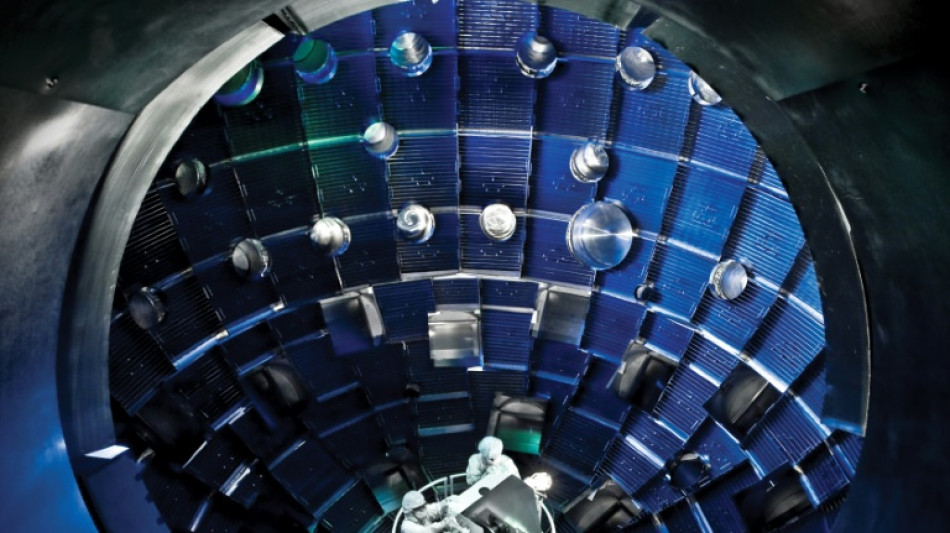
Nuclear fusion: harnessing the power of the stars
The US Department of Energy's nuclear fusion laboratory says there will be a "major scientific breakthrough" announced Tuesday, as media report that scientists have finally surpassed an important milestone for the technology: getting more energy out than was put in.
The announcement has the scientific community abuzz, as nuclear fusion is considered by some to be the energy of the future, particularly as it produces no greenhouse gases, leaves little waste and has no risk of nuclear accidents.
Here is an update on how nuclear fusion works, what projects are underway and estimates on when they could be completed:
- Energy of the stars -
Fusion differs from fission, the technique currently used in nuclear power plants, by fusing two atomic nuclei instead of splitting one.
In fact, fusion is the process that powers the sun.
Two light hydrogen atoms, when they collide at very high speeds, fuse together into one heavier element, helium, releasing energy in the process.
"Controlling the power source of the stars is the greatest technological challenge humanity has ever undertaken," tweeted physicist Arthur Turrell, author of "The Star Builders."
- Two distinct methods -
Producing fusion reactions on Earth is only possible by heating matter to extremely high temperatures -- over 100 million degrees Celsius (180 million Fahrenheit).
"So we have to find ways to isolate this extremely hot matter from anything that could cool it down. This is the problem of containment," Erik Lefebvre, project leader at the French Atomic Energy Commission (CEA), told AFP.
One method is to "confine" the fusion reaction with magnets.
In a huge donut-shaped reactor, light hydrogen isotopes (deuterium and tritium) are heated until they reach the state of plasma, a very low density gas.
Magnets confine the swirling plasma gas, preventing it from coming into contact with the chamber's walls, while the atoms collide and begin fusing.
This is the type of reactor used in the major international project known as ITER, currently under construction in France, as well as the Joint European Torus (JET) near Oxford, England.
A second method is inertial confinement fusion, in which high energy lasers are directed simultaneously into a thimble-sized cylinder containing the hydrogen.
This technique is used by the French Megajoule Laser (LMJ), and the world's most advanced fusion project, the California-based National Ignition Facility (NIF).
Inertial confinement is used to demonstrate the physical principles of fusion, while magnetic confinement seeks to mimic future industrial-scale reactors.
- State of research -
For decades, scientists have attempted to achieve what is known as "net energy gain" -- that is, more energy is produced by the fusion reaction than it takes to activate it.
According to reports by the Financial Times and the Washington Post, that will be the "major scientific breakthrough" announced Tuesday by the NIF.
But Lefebvre cautions that "the road is still very long" before "a demonstration on an industrial scale that is commercially viable."
He says such a project will take another 20 or 30 years to be completed.
To get there, researchers must first increase the efficiency of the lasers and reproduce the experiment more frequently.
- Fusion's benefits -
The NIF's reported success has sparked great excitement in the scientific community, which is hoping the technology could be a game-changer for global energy production.
Unlike fission, fusion carries no risk of nuclear accidents.
"If a few lasers are missing and they don't go off at the right time, or if the confinement of the plasma by the magnetic field... is not perfect," the reaction will simply stop, Lefebvre says.
Nuclear fusion also produces much less radioactive waste than current power plants, and above all, emits no greenhouse gases.
"It is an energy source that is totally carbon-free, generates very little waste, and is intrinsically extremely safe," according to Lefebvre, who says fusion could be "a future solution for the world's energy problems."
Regardless of Tuesday's announcement, however, the technology is still a far way off from producing energy on an industrial scale, and cannot therefore be relied on as an immediate solution to the climate crisis.
P.Serra--PC




