-
 Australian museum recovers Egyptian artefacts after break-in
Australian museum recovers Egyptian artefacts after break-in
-
India forced to defend US trade deal as doubts mount

-
 Bitter pill: Taliban govt shakes up Afghan medicine market
Bitter pill: Taliban govt shakes up Afghan medicine market
-
Crunch time for Real Madrid's Mbappe-Vinicius partnership

-
 Rio Carnival parades kick off with divisive ode to Lula in election year
Rio Carnival parades kick off with divisive ode to Lula in election year
-
Nepal 'addicted' to the trade in its own people

-
 Asian markets sluggish as Lunar New Year holiday looms
Asian markets sluggish as Lunar New Year holiday looms
-
'Pure extortion': foreign workers face violence and exploitation in Croatia

-
 Nepal launches campaigns for first post-uprising polls
Nepal launches campaigns for first post-uprising polls
-
What to know as South Korea ex-president Yoon faces insurrection verdict

-
 'Train Dreams,' 'The Secret Agent' nab Spirit wins to boost Oscars campaigns
'Train Dreams,' 'The Secret Agent' nab Spirit wins to boost Oscars campaigns
-
Rubio visits Trump's 'friend' Orban ahead of Hungary polls

-
 Kim unveils housing block for North Korean troops killed aiding Russia: KCNA
Kim unveils housing block for North Korean troops killed aiding Russia: KCNA
-
Accused Bondi killer Naveed Akram appears in court by video link

-
 Art and the deal: market slump pushes galleries to the Gulf
Art and the deal: market slump pushes galleries to the Gulf
-
Job threats, rogue bots: five hot issues in AI

-
 India hosts AI summit as safety concerns grow
India hosts AI summit as safety concerns grow
-
'Make America Healthy' movement takes on Big Ag, in break with Republicans

-
 Tech is thriving in New York. So are the rents
Tech is thriving in New York. So are the rents
-
Young USA Stars beat Stripes in NBA All-Star tourney final

-
 New anti-government chants in Tehran after giant rallies abroad: reports
New anti-government chants in Tehran after giant rallies abroad: reports
-
'The Secret Agent' nabs Spirit Awards win in boost to Oscars campaign

-
 Brignone wins second Milan-Cortina gold as Klaebo claims record ninth Olympic crown
Brignone wins second Milan-Cortina gold as Klaebo claims record ninth Olympic crown
-
Morikawa wins at Pebble Beach despite Scheffler heroics

-
 Germany's Hase and Volodin tango to Olympic pairs figure skating lead
Germany's Hase and Volodin tango to Olympic pairs figure skating lead
-
Rayo thrash Atletico who 'deserved to lose' as Betis cut gap

-
 Napoli salvage point after Malen twice puts Roma ahead
Napoli salvage point after Malen twice puts Roma ahead
-
Lyon down Nice to boost Ligue 1 title bid with 13th straight win

-
 LeBron still unclear on NBA future: 'I have no idea'
LeBron still unclear on NBA future: 'I have no idea'
-
Shelton battles back from brink to beat Fritz, take Dallas crown

-
 Great Britain celebrate best-ever Winter Olympics
Great Britain celebrate best-ever Winter Olympics
-
Brignone wins second Milan-Cortina gold as Klaebo claims record ninth

-
 Arteta concerned over Arsenal's mounting injury list
Arteta concerned over Arsenal's mounting injury list
-
In fuel-starved Cuba, the e-tricycle is king

-
 Shaidorov still spinning after outshining Malinin for Olympic gold
Shaidorov still spinning after outshining Malinin for Olympic gold
-
Late Gruda goal grabs Leipzig draw versus Wolfsburg

-
 'Ultra-left' blamed for youth's killing that shocked France
'Ultra-left' blamed for youth's killing that shocked France
-
Canada wrap up perfect Olympic ice hockey preliminary campaign

-
 Historical queer film 'Rose' shown at Berlin with call to action
Historical queer film 'Rose' shown at Berlin with call to action
-
Wales' Tandy tips hat to France after Six Nations hammering

-
 Quadruple chasing Arsenal rout Wigan to reach FA Cup fifth round
Quadruple chasing Arsenal rout Wigan to reach FA Cup fifth round
-
2026 S-Class starry facelift

-
 What they said as India beat Pakistan at T20 World Cup - reaction
What they said as India beat Pakistan at T20 World Cup - reaction
-
Away-day blues: England count cost of Scotland Six Nations defeat

-
 'Wuthering Heights' debuts atop North America box office
'Wuthering Heights' debuts atop North America box office
-
Rayo thrash Atletico who 'deserved to lose'

-
 Kok beats Leerdam in Olympic rematch of Dutch speed skaters
Kok beats Leerdam in Olympic rematch of Dutch speed skaters
-
India rout bitter rivals Pakistan by 61 runs at T20 World Cup

-
 France run rampant to thrash sorry Wales 54-12 in Six Nations
France run rampant to thrash sorry Wales 54-12 in Six Nations
-
Rio to kick off Carnival parade with ode to Lula in election year


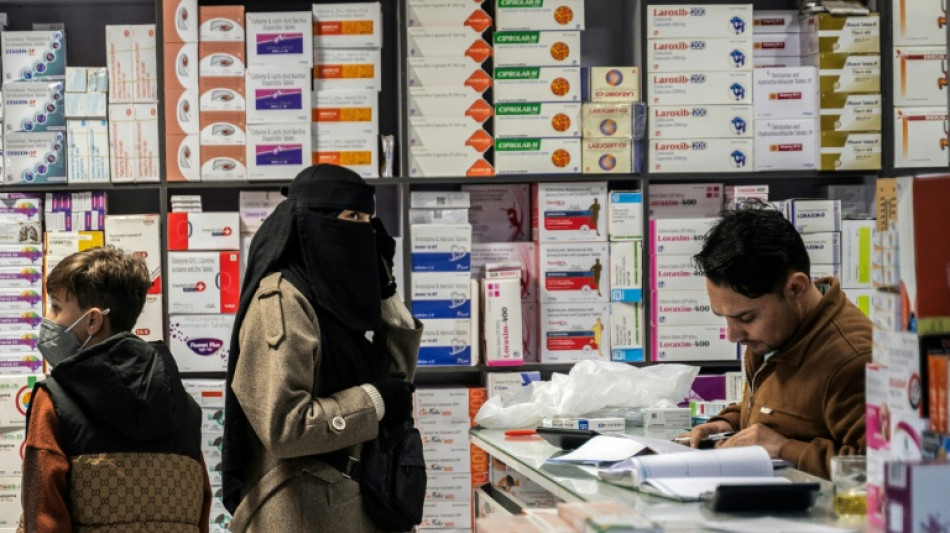
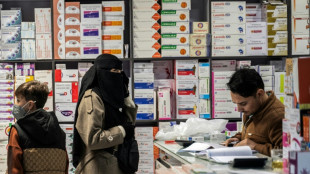
Bitter pill: Taliban govt shakes up Afghan medicine market
Afghanistan's decision to overhaul its medicine market was meant to improve quality and boost domestic production, but industry specialists say the swift changes have led to a litany of problems.
The Taliban authorities announced in November that the decades-long dependency on medicine imports from Pakistan would soon end, a step taken after deadly border clashes with their neighbour.
After the ban came into effect this month, finance ministry spokesman Abdul Qayoom Naseer told AFP that the government urged all importers to find "alternative and legal" sources to replace Pakistani supplies.
Despite a three-month grace period to end existing contracts and clear customs, the shift presents a huge challenge for a country which had imported more than half its medicine from Pakistan.
"Some of the prices have increased, some of them are short (unavailable), it has created a lot of problems for people," said Mujeebullah Afzali, a pharmacist in the capital, Kabul.
Drugs now have to come from elsewhere, increasing transit time and transport costs, and adding logistical complexities.
The pharmacist said he had begun importing medicine through the Islam Qala crossing on the Iranian border, "which increased the transportation fee 10 to 15 percent".
Transport costs used to account for six to seven percent of total spending on medicine, but this has now risen to 25 to 30 percent, said a person directly involved in the pharmaceutical industry, speaking to AFP on condition of anonymity due to security concerns.
He estimated that the overall losses to business owners had already reached millions of dollars.
"If a medicine was short in the market before, a call was made to Pakistan, and the medicine was delivered in two to three days," he said.
Whether legally or not, it was "delivered quickly", he added.
- 'Fill the gap' -
The illicit trade in pharmaceuticals was a key driver for the overhaul, according to the health ministry.
"The biggest problem with Pakistani medicine was that we used to receive counterfeit and fake medicines," ministry spokesman Sharafat Zaman told AFP.
He acknowledged it will take some time to shift the market, saying that officials were working with Iran, India, Bangladesh, Uzbekistan, Turkey, China and Belarus to source medicine.
"India was second in the market, which means that now, through Indian medicines, we can cover the percentage needed," Zaman said.
And domestic production of 600 medicines has "solved the problems" of many patients, he said.
Afghanistan already produces a variety of serums including antibiotics, according to manufacturer Milli Shifa Pharmaceutical.
The company makes 100,000 bottles daily and "can double the capability" if demand merits, CEO Nasar Ahmad Taraki told AFP.
While Afghanistan has significantly expanded its pharmaceutical sector, domestic output still only meets a small fraction of the overall demand.
The industry source told AFP that the need to import raw materials, the high energy costs and limited infrastructure mean the country cannot be entirely self-sufficient in medicine production.
"If we are provided with the facilities, then we would be able to fill the gap created by Pakistan's situation," he said.
- Shortages and higher costs -
But reshaping an industry nationwide takes more than three months.
Some drugs made in Afghanistan have proven more expensive than those imported from Pakistan, which over the years have gained consumers' trust.
Some people believe that "if they use Pakistani medicine, they will be cured" -- but not if it came from India "or any other country", the industry source said.
Physicians, meanwhile, are also struggling, a healthcare provider in Kabul told AFP.
Doctors "must change prescriptions, find suitable alternatives, and spend additional time adjusting treatment plans", he said, requesting anonymity for security reasons.
The shake-up, which ultimately is meant to end reliance on Pakistan, is complicating care in the short term and could delay treatment, he warned.
"Patients face medicine shortages, frequent switches to alternative products, and sometimes higher costs."
S.Pimentel--PC
