-
 Bethell spins England to 3-0 sweep over Sri Lanka in World Cup warm-up
Bethell spins England to 3-0 sweep over Sri Lanka in World Cup warm-up
-
Nagelsmann backs Ter Stegen for World Cup despite 'cruel' injury

-
 Homage or propaganda? Carnival parade stars Brazil's Lula
Homage or propaganda? Carnival parade stars Brazil's Lula
-
EU must be 'less naive' in COP climate talks: French ministry

-
 Colombia's Petro meets Trump after months of tensions
Colombia's Petro meets Trump after months of tensions
-
Air India inspects Boeing 787 fuel switches after grounding

-
 US envoy evokes transition to 'democratic' Venezuela
US envoy evokes transition to 'democratic' Venezuela
-
Syria govt forces enter Qamishli under agreement with Kurds

-
 WHO wants $1 bn for world's worst health crises in 2026
WHO wants $1 bn for world's worst health crises in 2026
-
France summons Musk, raids X offices as deepfake backlash grows

-
 Four out of every 10 cancer cases are preventable: WHO
Four out of every 10 cancer cases are preventable: WHO
-
Sacked UK envoy Mandelson quits parliament over Epstein ties

-
 US House to vote Tuesday to end partial government shutdown
US House to vote Tuesday to end partial government shutdown
-
Eswatini minister slammed for reported threat to expel LGBTQ pupils

-
 Pfizer shares drop on quarterly loss
Pfizer shares drop on quarterly loss
-
Norway's Kilde withdraws from Winter Olympics

-
 Vonn says 'confident' can compete at Olympics despite ruptured ACL
Vonn says 'confident' can compete at Olympics despite ruptured ACL
-
Germany acquires power grid stake from Dutch operator

-
 Finland building icebreakers for US amid Arctic tensions
Finland building icebreakers for US amid Arctic tensions
-
Petro extradites drug lord hours before White House visit

-
 Disney names theme parks boss chief Josh D'Amaro as next CEO
Disney names theme parks boss chief Josh D'Amaro as next CEO
-
Macron says work under way to resume contact with Putin

-
 Prosecutors to request bans from office in Le Pen appeal trial
Prosecutors to request bans from office in Le Pen appeal trial
-
Tearful Gazans finally reunite after limited Rafah reopening

-
 Iran president confirms talks with US after Trump's threats
Iran president confirms talks with US after Trump's threats
-
Spanish skater allowed to use Minions music at Olympics

-
 Fire 'under control' at bazaar in western Tehran
Fire 'under control' at bazaar in western Tehran
-
Howe trusts Tonali will not follow Isak lead out of Newcastle

-
 Vonn to provide injury update as Milan-Cortina Olympics near
Vonn to provide injury update as Milan-Cortina Olympics near
-
France summons Musk for 'voluntary interview', raids X offices

-
 US judge to hear request for 'immediate takedown' of Epstein files
US judge to hear request for 'immediate takedown' of Epstein files
-
Russia resumes large-scale strikes on Ukraine in glacial temperatures

-
 Fit-again France captain Dupont partners Jalibert against Ireland
Fit-again France captain Dupont partners Jalibert against Ireland
-
French summons Musk for 'voluntary interview' as authorities raid X offices

-
 IOC chief Coventry calls for focus on sport, not politics
IOC chief Coventry calls for focus on sport, not politics
-
McNeil's partner hits out at 'brutal' football industry after Palace move collapses

-
 Proud moment as Prendergast brothers picked to start for Ireland
Proud moment as Prendergast brothers picked to start for Ireland
-
Germany has highest share of older workers in EU

-
 Teen swims four hours to save family lost at sea off Australia
Teen swims four hours to save family lost at sea off Australia
-
Ethiopia denies Trump claim mega-dam was financed by US

-
 Russia resumes strikes on freezing Ukrainian capital ahead of talks
Russia resumes strikes on freezing Ukrainian capital ahead of talks
-
Malaysian court acquits French man on drug charges

-
 Switch 2 sales boost Nintendo results but chip shortage looms
Switch 2 sales boost Nintendo results but chip shortage looms
-
From rations to G20's doorstep: Poland savours economic 'miracle'

-
 Russia resumes strikes on freezing Ukrainian capital
Russia resumes strikes on freezing Ukrainian capital
-
'Way too far': Latino Trump voters shocked by Minneapolis crackdown

-
 England and Brook seek redemption at T20 World Cup
England and Brook seek redemption at T20 World Cup
-
Coach Gambhir under pressure as India aim for back-to-back T20 triumphs

-
 'Helmets off': NFL stars open up as Super Bowl circus begins
'Helmets off': NFL stars open up as Super Bowl circus begins
-
Japan coach Jones says 'fair' World Cup schedule helps small teams


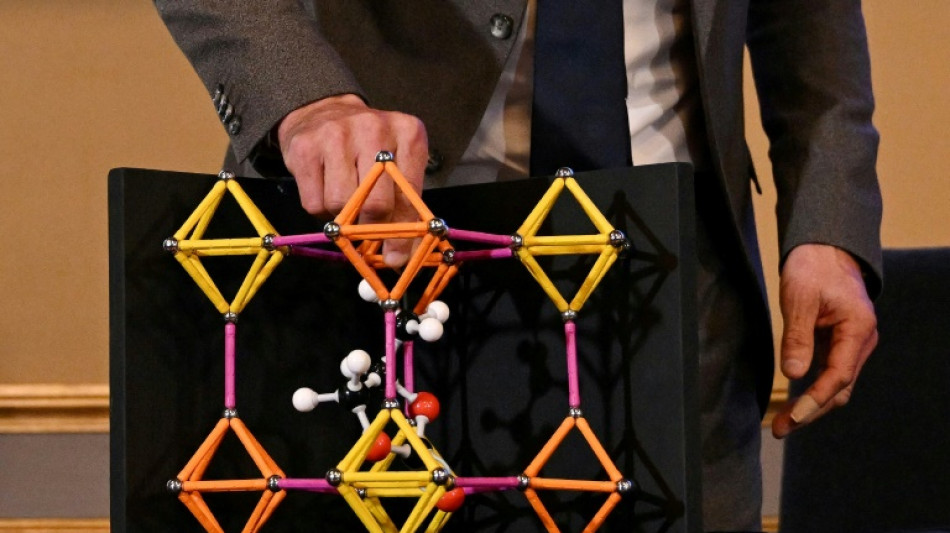
'Solids full of holes': Nobel-winning materials explained
The chemistry Nobel was awarded on Wednesday to three scientists who discovered a revolutionary way of making materials full of tiny holes that can do everything from sucking water out of the desert air to capturing climate-warming carbon dioxide.
The particularly roomy molecular architecture, called metal-organic frameworks, has also allowed scientists to filter "forever chemicals" from water, smuggle drugs into bodies -- and even slow the ripening of fruit.
After Japan's Susumu Kitagawa, UK-born Richard Robson and American-Jordanian Omar Yaghi won their long-anticipated Nobel Prize, here is what you need to know about their discoveries.
- What are metal-organic frameworks? -
Imagine you turn on the hot water for your morning shower, David Fairen-Jimenez, a professor who studies metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) at the University of Cambridge, told AFP.
The mirror in your bathroom fogs up as water molecules collect on its flat surface -- but it can only absorb so much.
Now imagine this mirror was made of a material that was extremely porous -- full of tiny holes -- and these holes were "the size of a water molecule," Fairen-Jimenez said.
This material would be able to hold far more water -- or other gases -- than seems possible.
At the Nobel ceremony, this secret storage ability was compared to Hermione's magical handbag in Harry Potter.
The inside space of a couple of grams of a particular MOF "holds an area as big as a football pitch," the Nobels said in a statement.
Ross Forgan, a professor of materials chemistry at the University of Glasgow, told AFP to think of MOFs as "solids that are full of holes".
They could look essentially like table salt, but "they have a ridiculously high storage capacity inside them because they are hollow -- they can soak up other molecules like a sponge."
- What did the Nobel-winners do? -
In the 1980s, Robson taught his students at Australia's University of Melbourne about molecular structures using wooden balls that played the role of atoms, connected by rods representing chemical bonds.
One day this inspired him to try to link different kinds of molecules together. By 1989, he had drawn out a crystal structure similar to a diamond's -- except that it was full of massive holes.
French researcher David Farrusseng compared the structure of MOFs to the Eiffel Tower. "By interlocking all the iron beams -- horizontal, vertical, and diagonal -- we see cavities appear," he told AFP.
However Robson's holey structures were unstable, and it took years before anyone could figure out what to do with them.
In 1997, Kitagawa finally managed to show that a MOF could absorb and release methane and other gases.
It was Yaghi who coined the term metal-organic frameworks and demonstrated to the world just how much room there was in materials made from them.
- What can they do? -
Because these frameworks can be assembled in different ways -- somewhat like playing with Lego -- companies and labs around the world have been testing out their capabilities.
"This is a field that's generating incredible enthusiasm and is moving extremely fast," Thierry Loiseau of French research centre CNRS told AFP.
More than 100,000 different kinds have already been reported in scientific literature, according to a Cambridge University database.
"Every single month, there are 500 new MOFs," Fairen-Jimenez said.
He and Forgan agreed that likely the greatest impact MOFs will have on the world are in the areas of capturing carbon and delivering drugs.
Though much hyped, efforts to capture carbon dioxide -- the driver of human-caused global warming -- have so far failed to live up to their promise.
Forgan said he was once "a bit sceptical about carbon capture, but now we're finally refining (the MOFs) to the point where they are meeting all the industrial requirements".
Canadian chemical producer BASF says it is the first company to produce hundreds of tons of MOFs a year, for carbon capture efforts.
And Yaghi himself has demonstrated that a MOF material was able to harvest water vapour from the night air in the desert US state of Arizona.
Once the rising Sun heated up the material, his team collected the drinkable water.
P.Queiroz--PC