-
 Howe trusts Tonali will not follow Isak lead out of Newcastle
Howe trusts Tonali will not follow Isak lead out of Newcastle
-
Vonn to provide injury update as Milan-Cortina Olympics near

-
 France summons Musk for 'voluntary interview', raids X offices
France summons Musk for 'voluntary interview', raids X offices
-
US judge to hear request for 'immediate takedown' of Epstein files

-
 Russia resumes large-scale strikes on Ukraine in glacial temperatures
Russia resumes large-scale strikes on Ukraine in glacial temperatures
-
Fit-again France captain Dupont partners Jalibert against Ireland

-
 French summons Musk for 'voluntary interview' as authorities raid X offices
French summons Musk for 'voluntary interview' as authorities raid X offices
-
IOC chief Coventry calls for focus on sport, not politics

-
 McNeil's partner hits out at 'brutal' football industry after Palace move collapses
McNeil's partner hits out at 'brutal' football industry after Palace move collapses
-
Proud moment as Prendergast brothers picked to start for Ireland

-
 Germany has highest share of older workers in EU
Germany has highest share of older workers in EU
-
Teen swims four hours to save family lost at sea off Australia

-
 Ethiopia denies Trump claim mega-dam was financed by US
Ethiopia denies Trump claim mega-dam was financed by US
-
Russia resumes strikes on freezing Ukrainian capital ahead of talks

-
 Malaysian court acquits French man on drug charges
Malaysian court acquits French man on drug charges
-
Switch 2 sales boost Nintendo results but chip shortage looms

-
 From rations to G20's doorstep: Poland savours economic 'miracle'
From rations to G20's doorstep: Poland savours economic 'miracle'
-
Russia resumes strikes on freezing Ukrainian capital

-
 'Way too far': Latino Trump voters shocked by Minneapolis crackdown
'Way too far': Latino Trump voters shocked by Minneapolis crackdown
-
England and Brook seek redemption at T20 World Cup

-
 Coach Gambhir under pressure as India aim for back-to-back T20 triumphs
Coach Gambhir under pressure as India aim for back-to-back T20 triumphs
-
'Helmets off': NFL stars open up as Super Bowl circus begins

-
 Japan coach Jones says 'fair' World Cup schedule helps small teams
Japan coach Jones says 'fair' World Cup schedule helps small teams
-
Do not write Ireland off as a rugby force, says ex-prop Ross

-
 Winter Olympics 2026: AFP guide to Alpine Skiing races
Winter Olympics 2026: AFP guide to Alpine Skiing races
-
Winter Olympics to showcase Italian venues and global tensions

-
 Buoyant England eager to end Franco-Irish grip on Six Nations
Buoyant England eager to end Franco-Irish grip on Six Nations
-
China to ban hidden car door handles in industry shift

-
 Sengun leads Rockets past Pacers, Ball leads Hornets fightback
Sengun leads Rockets past Pacers, Ball leads Hornets fightback
-
Waymo raises $16 bn to fuel global robotaxi expansion

-
 Netflix to livestream BTS comeback concert in K-pop mega event
Netflix to livestream BTS comeback concert in K-pop mega event
-
Rural India powers global AI models

-
 Equities, metals, oil rebound after Asia-wide rout
Equities, metals, oil rebound after Asia-wide rout
-
Bencic, Svitolina make history as mothers inside tennis top 10

-
 Italy's spread-out Olympics face transport challenge
Italy's spread-out Olympics face transport challenge
-
Son of Norway crown princess stands trial for multiple rapes

-
 Side hustle: Part-time refs take charge of Super Bowl
Side hustle: Part-time refs take charge of Super Bowl
-
Paying for a selfie: Rome starts charging for Trevi Fountain

-
 Faced with Trump, Pope Leo opts for indirect diplomacy
Faced with Trump, Pope Leo opts for indirect diplomacy
-
NFL chief expects Bad Bunny to unite Super Bowl audience

-
 Australia's Hazlewood to miss start of T20 World Cup
Australia's Hazlewood to miss start of T20 World Cup
-
Bill, Hillary Clinton to testify in US House Epstein probe

-
 Cuba confirms 'communications' with US, but says no negotiations yet
Cuba confirms 'communications' with US, but says no negotiations yet
-
From 'watch his ass' to White House talks for Trump and Petro

-
 Trump says not 'ripping' down Kennedy Center -- much
Trump says not 'ripping' down Kennedy Center -- much
-
Sunderland rout 'childish' Burnley

-
 Musk merges xAI into SpaceX in bid to build space data centers
Musk merges xAI into SpaceX in bid to build space data centers
-
Former France striker Benzema switches Saudi clubs

-
 Sunderland rout hapless Burnley
Sunderland rout hapless Burnley
-
Costa Rican president-elect looks to Bukele for help against crime


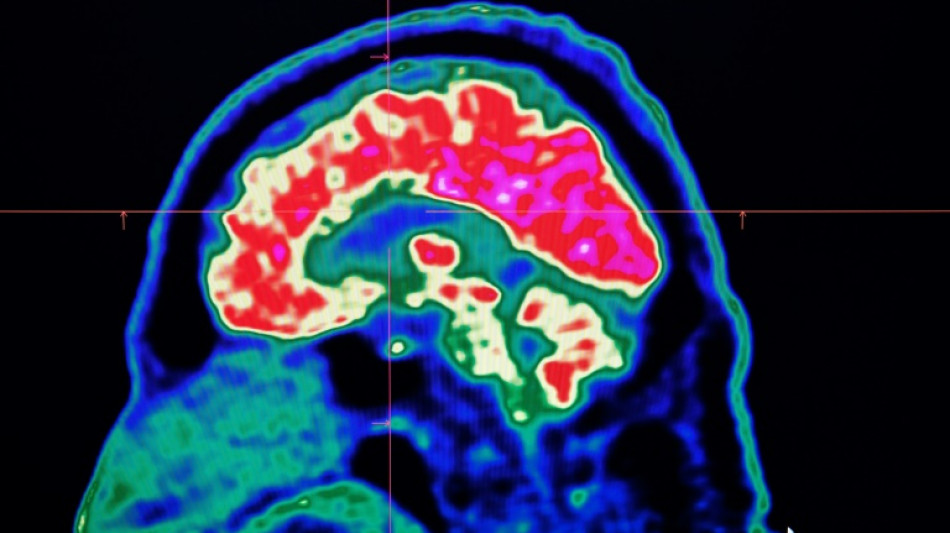
What are all these microplastics doing to our brains?
Tiny shards of plastic called microplastics have been detected accumulating in human brains, but there is not yet enough evidence to say whether this is doing us harm, experts have said.
These mostly invisible pieces of plastic have been found everywhere from the top of mountains to the bottom of oceans, in the air we breathe and the food we eat. They have also been discovered riddled throughout human bodies, inside lungs, hearts, placentas and even crossing the blood-brain barrier.
The increasing ubiquity of microplastics has become a key issue in efforts to hammer out the world's first plastic pollution treaty, with the latest round of UN talks being held in Geneva next week.
The effects that microplastics and even smaller nanoplastics have on human health is not yet fully understood, but researchers have been working to find out more in this relatively new field.
The most prominent study looking at microplastics in brains was published in the journal Nature Medicine in February.
The scientists tested brain tissue from 28 people who died in 2016 and 24 who died last year in the US state of New Mexico, finding that the amount of microplastics in the samples increased over time.
The study made headlines around the world when the lead researcher, US toxicologist Matthew Campen, told the media that they detected the equivalent of a plastic spoon's worth of microplastics in the brains.
Campen also told Nature that he estimated the researchers could isolate around 10 grammes of plastic from a donated human brain -- comparing that amount to an unused crayon.
- Speculation 'far beyond the evidence' -
But other researchers have since urged caution about the small study.
"While this is an interesting finding, it should be interpreted cautiously pending independent verification," toxicologist Theodore Henry of Scotland's Heriot-Watt University told AFP.
"Currently, the speculation about the potential effects of plastic particles on health go far beyond the evidence," he added.
Oliver Jones, a chemistry professor at Australia's RMIT University, told AFP there was "not enough data to make firm conclusions on the occurrence of microplastics in New Mexico, let alone globally".
He also found it "rather unlikely" that brains could contain more microplastics than has been found in raw sewage -- as the researchers had estimated.
Jones pointed out the people in the study were perfectly healthy before they died, and that the researchers acknowledged there was not enough data to show that the microplastics caused harm.
"If (and it is a big if in my view) there are microplastics in our brains, there is as yet no evidence of harm," Jones added.
The study also contained duplicated images, the neuroscience news website The Transmitter has reported, though experts said this did not affect its main findings.
- 'Cannot wait for complete data' -
Most of the research into the effects microplastics have on health has been observational, which means it cannot establish cause and effect.
One such study, published in the New England Journal of Medicine last year, found that microplastics building up in blood vessels was linked to an increased risk of heart attack, stroke and death in patients with a disease that clogs arteries.
There have also been experiments carried out on mice, including a study in Science Advances in January which detected microplastics in their brains.
The Chinese researchers said that microplastics can cause rare blood clots in the brains of mice by obstructing cells -- while emphasising that the small mammals are very different to humans.
A review by the World Health Organization in 2022 found that the "evidence is insufficient to determine risks to human health" from microplastics.
However many health experts have cited the precautionary principle, saying the potential threat microplastics could pose requires action.
A report on the health risks of microplastics by the Barcelona Institute for Global Health published this week ahead of the treaty talks said that "policy decisions cannot wait for complete data".
"By acting now to limit exposure, improve risk assessment methodologies, and prioritise vulnerable populations, we can address this pressing issue before it escalates into a broader public health crisis," it added.
The amount of plastic the world produces has doubled since 2000 -- and is expected to triple from current rates by 2060.
M.Gameiro--PC



