-
 Trump signs spending bill ending US government shutdown
Trump signs spending bill ending US government shutdown
-
Arsenal sink Chelsea to reach League Cup final

-
 Leverkusen sink St Pauli to book spot in German Cup semis
Leverkusen sink St Pauli to book spot in German Cup semis
-
'We just need something positive' - Monks' peace walk across US draws large crowds

-
 Milan close gap on Inter with 3-0 win over Bologna
Milan close gap on Inter with 3-0 win over Bologna
-
No US immigration agents at Super Bowl: security chief

-
 NASA Moon mission launch delayed to March after test
NASA Moon mission launch delayed to March after test
-
Spain to seek social media ban for under-16s

-
 LIV Golf events to receive world ranking points: official
LIV Golf events to receive world ranking points: official
-
US House passes spending bill ending government shutdown

-
 US jet downs Iran drone but talks still on course
US jet downs Iran drone but talks still on course
-
UK police launching criminal probe into ex-envoy Mandelson

-
 US-Iran talks 'still scheduled' after drone shot down: White House
US-Iran talks 'still scheduled' after drone shot down: White House
-
Chomsky sympathized with Epstein over 'horrible' press treatment

-
 French prosecutors stick to demand for five-year ban for Le Pen
French prosecutors stick to demand for five-year ban for Le Pen
-
Russia's economic growth slowed to 1% in 2025: Putin

-
 Bethell spins England to 3-0 sweep over Sri Lanka in World Cup warm-up
Bethell spins England to 3-0 sweep over Sri Lanka in World Cup warm-up
-
Nagelsmann backs Ter Stegen for World Cup despite 'cruel' injury

-
 Homage or propaganda? Carnival parade stars Brazil's Lula
Homage or propaganda? Carnival parade stars Brazil's Lula
-
EU must be 'less naive' in COP climate talks: French ministry

-
 Colombia's Petro meets Trump after months of tensions
Colombia's Petro meets Trump after months of tensions
-
Air India inspects Boeing 787 fuel switches after grounding

-
 US envoy evokes transition to 'democratic' Venezuela
US envoy evokes transition to 'democratic' Venezuela
-
Syria govt forces enter Qamishli under agreement with Kurds

-
 WHO wants $1 bn for world's worst health crises in 2026
WHO wants $1 bn for world's worst health crises in 2026
-
France summons Musk, raids X offices as deepfake backlash grows

-
 Four out of every 10 cancer cases are preventable: WHO
Four out of every 10 cancer cases are preventable: WHO
-
Sacked UK envoy Mandelson quits parliament over Epstein ties

-
 US House to vote Tuesday to end partial government shutdown
US House to vote Tuesday to end partial government shutdown
-
Eswatini minister slammed for reported threat to expel LGBTQ pupils

-
 Pfizer shares drop on quarterly loss
Pfizer shares drop on quarterly loss
-
Norway's Kilde withdraws from Winter Olympics

-
 Vonn says 'confident' can compete at Olympics despite ruptured ACL
Vonn says 'confident' can compete at Olympics despite ruptured ACL
-
Germany acquires power grid stake from Dutch operator

-
 Finland building icebreakers for US amid Arctic tensions
Finland building icebreakers for US amid Arctic tensions
-
Petro extradites drug lord hours before White House visit

-
 Disney names theme parks boss chief Josh D'Amaro as next CEO
Disney names theme parks boss chief Josh D'Amaro as next CEO
-
Macron says work under way to resume contact with Putin

-
 Prosecutors to request bans from office in Le Pen appeal trial
Prosecutors to request bans from office in Le Pen appeal trial
-
Tearful Gazans finally reunite after limited Rafah reopening

-
 Iran president confirms talks with US after Trump's threats
Iran president confirms talks with US after Trump's threats
-
Spanish skater allowed to use Minions music at Olympics

-
 Fire 'under control' at bazaar in western Tehran
Fire 'under control' at bazaar in western Tehran
-
Howe trusts Tonali will not follow Isak lead out of Newcastle

-
 Vonn to provide injury update as Milan-Cortina Olympics near
Vonn to provide injury update as Milan-Cortina Olympics near
-
France summons Musk for 'voluntary interview', raids X offices

-
 US judge to hear request for 'immediate takedown' of Epstein files
US judge to hear request for 'immediate takedown' of Epstein files
-
Russia resumes large-scale strikes on Ukraine in glacial temperatures

-
 Fit-again France captain Dupont partners Jalibert against Ireland
Fit-again France captain Dupont partners Jalibert against Ireland
-
French summons Musk for 'voluntary interview' as authorities raid X offices


Webb Telescope: What will scientists learn?
The James Webb Space Telescope's first images aren't just breathtaking -- they contain a wealth of scientific insights and clues that researchers are eager to pursue.
Here are some of the things scientists now hope to learn.
- Into the deep -
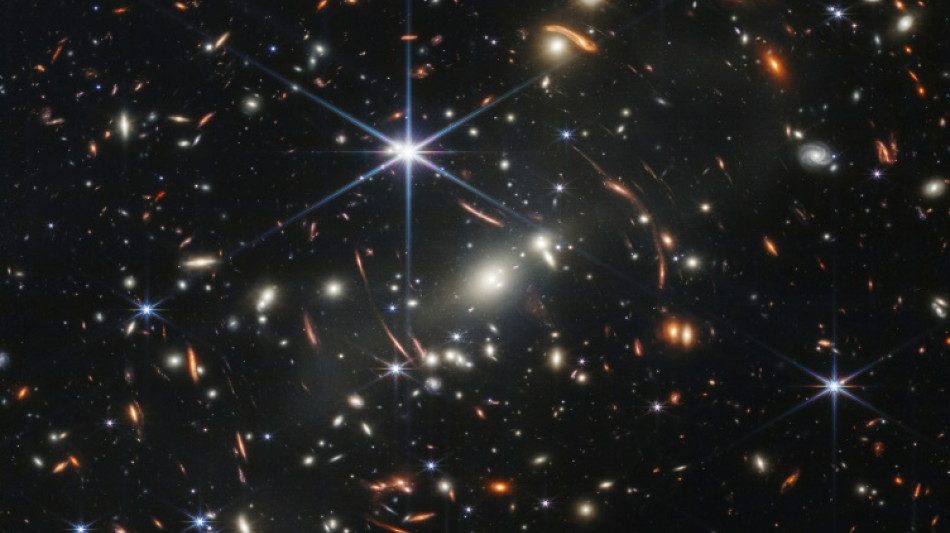
Webb's first image, released Monday, delivered the deepest and sharpest infrared image of the distant universe so far, "Webb's First Deep Field."
The white circles and ellipses are from the galaxy cluster in the foreground called SMACS 0723, as it appeared more than 4.6 billion years ago -- roughly when our Sun formed too.
The reddish arcs are from light from ancient galaxies that has traveled more than 13 billion years, bending around the foreground cluster, which acts as a gravitational lens.
NASA astrophysicist Amber Straughn said she was struck by "the astounding detail that you can see in some of these galaxies."
"They just pop out! There is so much more detail, it's like seeing in high-def."
Plus, added NASA astrophysicist Jane Rigby, the image can teach us more about mysterious dark matter, which is thought to comprise 85 percent of matter in the universe -- and is the main cause of the cosmic magnifying effect.
The composite image, which required a 12.5 hour exposure time, is considered a practice run. Given longer exposure time, Webb should break all-time distance records by gazing back to the first few hundred million years after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago.
- The hunt for habitable planets -
Webb captured the signature of water, along with previously undetected evidence of clouds and haze, in the atmosphere surrounding a hot, puffy gas giant planet called WASP-96 b that orbits a distant star like our Sun.
The telescope achieved this by analyzing starlight filtered through the planet's atmosphere as it moves across the star, to the unfiltered starlight detected when the planet is beside the star -- a technique called spectroscopy that no other instrument can do at the same detail.
WASP-96 b is one of more than 5,000 confirmed exoplanets in the Milky Way. But what really excites astronomers is the prospect of pointing Webb at smaller, rocky worlds, like our own Earth, to search for atmospheres and bodies of liquid water that could support life.
- Death of a star -
Webb's cameras captured a stellar graveyard, in the Southern Ring Nebula, revealing the dim, dying star at its center in clear detail for the first time, and showing that it is cloaked in dust.
Astronomers will use Webb to delve deeper into specifics about "planetary nebulae" like these, which spew out clouds of gas and dust.
These nebulae will eventually also lead to rebirth.
The gas and cloud ejection stops after some tens of thousands of years, and once the material is scattered in space, new stars can form.
- A cosmic dance -
Stephan's Quintet, a grouping of five galaxies, is located in the constellation Pegasus.
Webb was able to pierce through the clouds of dust and gas at the center of the galaxy to glean new insights, such as the velocity and composition of outflows of gas near its supermassive black hole.
Four of the galaxies are close together and locked in a "cosmic dance" of repeated close encounters.
By studying it, "you learn how the galaxies collide and merge," said cosmologist John Mather, adding our own Milky Way was probably assembled out of 1,000 smaller galaxies.
Understanding the black hole better will also give us greater insights into Sagittarius A*, the black hole at the center of the Milky Way, which is shrouded in dust.
- Stellar nursey -
Perhaps the most beautiful image is that of the "Cosmic Cliffs" from the Carina Nebula, a stellar nursery.
Here, for the first time, Webb has revealed previously invisible regions of star formation, which will tell us more about why stars form with certain mass, and what determines the number that form in a certain region.
They may look like mountains, but the tallest of the craggy peaks are seven light years high, and the yellow structures are made from huge hydrocarbon molecules, said Webb project scientist Klaus Pontoppidan.
In addition to being the stuff of stars, nebular material could also be where we come from.
"This may be the way that the universe is transporting carbon, the carbon that we're made of, to planets that may be habitable for life," he said.
- The great unknown -
Perhaps most exciting of all is journeying into the unknown, said Straughn.
Hubble played a key role in discovering that dark energy is causing the universe to expand at an ever-growing rate, "so it's hard to imagine what we might learn with this 100 times more powerful instrument."
O.Gaspar--PC